Dr. Preetesh Choudhary: Your Trusted Knee Specialist in Indore
Dr. Preetesh Choudhary is a leading orthopedic doctor and the Best Doctor for Knee Pain in Indore, Madhya Pradesh, with nearly a decade of experience in helping patients regain their mobility and live active lives. He is dedicated to providing comprehensive and compassionate care for a wide range of knee conditions, from minor injuries to complex joint replacements.
Knee joint preservation is the process of restoring the knee joint to its normal range of motion and functionality without the need for replacement. orthopedic doctor can treat knee joint issues while keeping the healthy structure of the damaged joints by using a preservation strategy. The majority of people who require knee joint preservation techniques have abnormalities in the knee’s articular cartilage.
Restoration of articular cartilage provides pain relief, enhances everyday performance, and in some circumstances can even stop or delay the onset of arthritis in the knee joint.
Best Doctor for knee injury in Indore
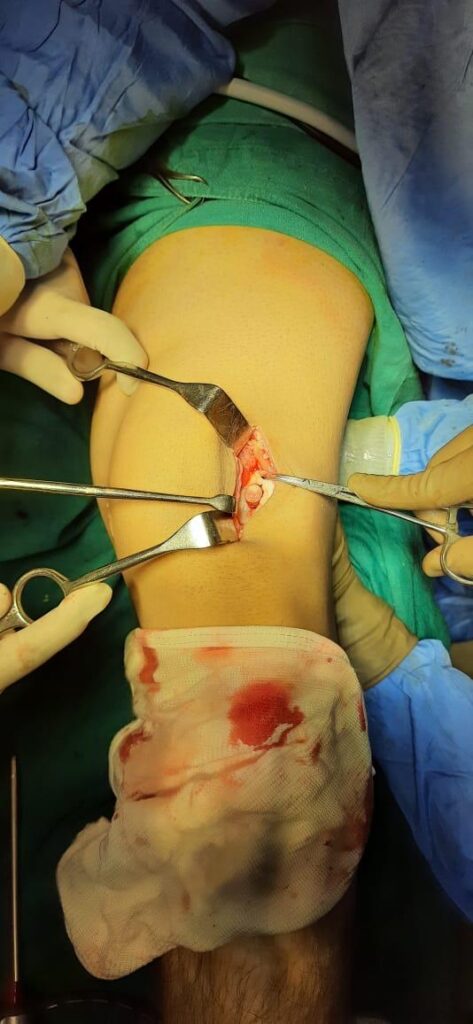
Options of Knee Preservation
Our healthcare professionals may employ either non-surgical or surgical methods to maintain the health of your knee. The most suitable treatment option for you will be determined by various factors, such as:
- The severity of cartilage deterioration;
- The nature of the knee injury; and
- Your age, general well-being, and level of physical activity.
Surgery for Knee Preservation
Individuals under the age of 50 might be eligible for procedures aimed at repairing knee cartilage. These interventions aim to rejuvenate knee cartilage using either the patient’s tissue or tissue from a donor (harvested from a deceased donor).
interventions aim to rejuvenate knee cartilage using either the patient’s tissue or tissue from a donor (harvested from a deceased donor).
Additional procedures you might undergo include:
- Ligament Repair or Reconstruction: During ligament surgery, your orthopedic surgeon will either reattach or reconstruct a torn ligament. Younger patients with cartilage issues often also have ligament injuries. For instance, if you’ve torn your anterior cruciate ligament (ACL), you might undergo ACL reconstruction.
- Osteotomy: This surgical procedure involves realigning bones to alleviate pressure on the injured knee. Osteotomy may be performed independently or alongside a cartilage restoration procedure.
- Partial Knee Replacement: In this procedure, the damaged part of the knee is replaced. Individuals under 60 may opt for a partial knee replacement to postpone or avoid the need for a total knee replacement.
Rehabilitation Following Knee Joint Preservation Surgery
Effective joint preservation surgery is complemented by a comprehensive postoperative rehabilitation program and regular physical therapy to maintain range of motion, reengage muscles, and reduce postoperative swelling.
Following any cartilage repair procedure, healing and recovery typically require 6-8 weeks. Additional aids such as crutches may be necessary for several weeks. Patients can begin improving their range of motion and building muscle strength after two weeks, and high-intensity activities like running may be resumed after four to six months once the bone has fully healed.
The success of joint preservation surgery largely hinges on adhering to a personalized therapy plan post-surgery under the guidance of a physical therapist. Optimal outcomes are achievable only through diligent adherence to a structured rehabilitation regimen, as failure to do so may lead to stiffness, scarring, and muscle weakening.
The actual recovery timeline varies widely among individuals and is influenced by factors such as overall health and the specific preservation technique employed.
Is Knee Joint Preservation Surgery Safe? What Are the Risks?
Overall, knee joint preservation surgery is considered a relatively safe procedure with a low incidence of complications. However, like any surgical intervention, there are general and individual-specific risks to consider. Some commonly encountered risks include:
- Unintentional damage to surrounding tissues
- Risk of infection
- Potential for bleeding
- Pain and swelling post-surgery
- Side effects associated with anesthesia
Conclusion:
Joint preservation employs non-surgical or minimally invasive surgical methods to maintain a deteriorating joint’s natural function and structure, aiming to delay or avoid joint replacement surgery as much as possible. These procedures offer faster recovery and lower complication risks due to minimal damage to surrounding tissues.
Dr. Preetesh Choudhary, orthopedic doctor excel in techniques prioritizing bone and function preservation.