Hip Impingement (FAI) in Young Adults- Symptoms and Surgical Treatment

Hip pain is no longer just a concern for the elderly. Increasingly, young adults are reporting hip discomfort and restricted mobility—often caused by a condition called Femoroacetabular Impingement (FAI) or simply hip impingement. If left untreated, this condition can lead to long-term joint damage and even early-onset arthritis.
In this blog, Dr. Preetesh Choudhary,one of Top 10 Hip Surgeons in India, explains the symptoms of hip impingement in young adults and explore the surgical treatment options available to help you regain pain-free movement.
What Is Hip Impingement (FAI)?
Hip impingement, medically known as Femoroacetabular Impingement (FAI), is a condition where there is abnormal contact between the bones of the hip joint. This can result in pain, stiffness, and damage to the cartilage inside the hip.
The hip is a ball-and-socket joint. In FAI, either the ball (femoral head), the socket (acetabulum), or both have an irregular shape. These bony abnormalities can cause the bones to rub against each other during movement, leading to joint damage over time.
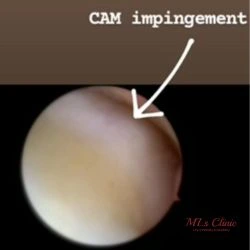
There are three types of FAI:
- Cam impingement – Caused by extra bone on the femoral head.
- Pincer impingement – Caused by extra bone on the acetabulum (hip socket).
- Combined impingement – A mix of both cam and pincer types.
Why Does FAI Occur in Young Adults?
FAI often develops in active individuals or athletes during their teenage years as their bones are still developing. Repetitive stress on the hip joint can cause extra bone growth, especially in sports like football, hockey, dancing, or martial arts.
Some contributing factors include:
- Genetics
- Structural abnormalities
- High-impact physical activities during growth years
- Repetitive hip flexion
FAI is increasingly recognized in young adults between the ages of 20 to 40, especially those leading an active lifestyle or with a history of sports-related injuries.
Recognizing the Symptoms:
The symptoms of hip impingement can vary from person to person, but young adults often experience one or more of the following:
- Groin Pain: This is the most common symptom and is often described as a deep ache or sharp pain located in the front of the hip or groin area. The pain may radiate to the side of the hip, the buttock, or even down the thigh.
- Pain with Activity: Symptoms are often aggravated by activities that involve hip flexion, such as running, jumping, squatting, twisting, and even prolonged sitting, especially in low chairs or cars.
- Stiffness and Limited Range of Motion: You might notice difficulty rotating your hip, especially internally (turning the foot inward). Getting in and out of cars, putting on shoes and socks, or bending at the waist can become challenging.
- Clicking, Catching, or Locking Sensation: Some individuals may experience a clicking, popping, snapping, or a feeling that their hip is catching or locking during movement.
- Pain After Exercise: Pain may persist or worsen after physical activity.
- Giving Way Sensation: In some cases, you might feel a sense of instability or that your hip is giving way.
How Is Hip Impingement Diagnosed?
Accurate diagnosis is the first step toward effective treatment. At MLS Clinic, Dr. Preetesh Choudhary, leading orthopedic surgeon, follows a thorough approach to diagnosing FAI, which includes:
- Medical History– we’ll discuss any previous hip issues or related leg/back injuries, even seemingly minor ones, as they can contribute to current pain. We’ll also review what you’ve already tried (rest, medications, therapy, etc.) and how effective they were.
- Physical Examination- During a physical examination for hip impingement, we will observe your movement and posture, feel around your hip for areas of tenderness, and assess how far you can move your hip in different directions to check your range of motion. Specific tests, such as the FADDIR test, may also be performed to reproduce your symptoms and help identify signs of impingement.
- Imaging Studies:
- X-rays: These are essential to visualize the shape of the femur and acetabulum and identify any bony abnormalities characteristic of cam or pincer impingement.
- MRI (Magnetic Resonance Imaging): MRI provides detailed images of the soft tissues, including the labrum and articular cartilage, allowing us to assess for tears or damage caused by the impingement. Sometimes, an MR arthrogram, where contrast dye is injected into the hip joint before the MRI, may be used for even better visualization of the labrum.
- CT Scan (Computed Tomography): In some complex cases, a CT scan may be used to provide a more detailed assessment of the bony anatomy.
Non-Surgical Treatment Options
Non-surgical treatment is considered for mild to moderate cases. These include:
- Activity modification – Avoiding movements that trigger hip pain. This helps reduce stress on the joint and prevents further irritation.
- Physical therapy – Strengthening surrounding muscles and improving hip mobility. Targeted exercises can restore function and improve joint stability.
- Anti-inflammatory medications – Reducing pain and swelling. These medications help manage symptoms and make daily activities more comfortable.
- Injections – Corticosteroids or platelet-rich plasma (PRP) for temporary relief. These can reduce inflammation and offer short-term pain control when other methods are not effective.
Surgical Treatment Options
When non-surgical treatments like rest, activity modification, pain medication, and physical therapy fail to provide adequate relief, surgical intervention may be necessary to address the underlying bony abnormalities and repair any damage within the joint. The primary goal of surgery is to reshape the femur and/or acetabulum to eliminate the abnormal contact and prevent further damage.
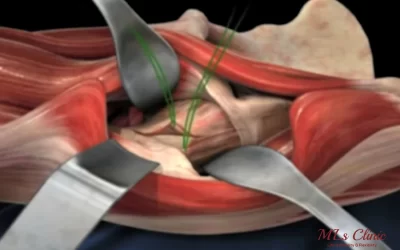
The gold standard for treating hip impingement in young adults is hip arthroscopy. This minimally invasive surgical technique involves making small incisions around the hip joint and inserting a tiny camera (arthroscope) and specialized surgical instruments. This allows us to visualize the inside of the joint on a video monitor and perform the necessary repairs and reshaping without the need for a large open incision.

Key Surgical Steps:
- Removal of excess bone from the femoral head or acetabulum
- Labral repair or reconstruction if there’s a tear
- Smoothing cartilage surfaces to reduce friction
- Restoring normal hip anatomy
Dr. Preetesh Choudhary at MLS Clinic is an expert in hip preservation techniques and performs hip arthroscopy with high precision to ensure minimal damage and faster recovery.
Recovery after Hip Impingement
Recovery following surgery for hip impingement (FAI) largely depends on the severity of the condition and the type of surgical repair performed, whether arthroscopic or open surgery. While every patient heals at their own pace, some general timelines and milestones that can be expected:
- Hospital Stay: Most arthroscopic hip surgeries are performed as day-care procedures, meaning the patient can return home the same day. In some cases, particularly when more extensive repair is needed, a one-night hospital stay may be recommended for monitoring and pain control.
- Use of Crutches: After surgery, patients are advised to use crutches for about 1 to 2 weeks. This helps reduce weight-bearing pressure on the healing joint and ensures proper post-operative joint protection.
- Physical Therapy: A structured physical therapy program is crucial and typically starts with gentle range-of-motion exercises to prevent stiffness. Gradually, strength training and mobility exercises are added to rebuild muscle support around the hip joint.
- Return to Activities: Patients can usually resume light activities such as walking and desk work within 4 to 6 weeks post-surgery. However, returning to high-impact sports or intense physical activities generally takes about 3 to 6 months.
- Long-Term Outlook: Most patients experience significant relief from pain and improved hip function within the first few weeks of surgery. With proper adherence to post-operative instructions and consistent rehabilitation, the long-term outcomes are excellent.
Conclusion
In conclusion, hip impingement (FAI) in young adults is a common yet often overlooked condition that can lead to chronic pain and early joint damage if not addressed in time. Early diagnosis and the right treatment—whether through lifestyle changes, physiotherapy, or surgical correction—can make a significant difference in restoring function and preventing further complications. Paying attention to symptoms and seeking expert care is essential for maintaining long-term joint health and leading an active, pain-free life. Don’t let hip pain hold you back—take the first step toward recovery with proper medical guidance.
Why should I choose MLS Clinic for Hip Treatment?
Because you’ll get:
- 18+ Years of Expertise:
Dr. Preetesh Choudhary, brings extensive experience in treating complex joint conditions, ensuring high-quality care and successful outcomes. - Accurate Diagnosis with Advanced Imaging:
We use the latest MRI and CT scans to pinpoint the exact cause of your hip pain, ensuring precise treatment from the start. - Advanced Surgical Techniques for Quicker Recovery:
Our state-of-the-art surgical methods reduce recovery time, minimize complications, and help you get back to your routine sooner. - Comprehensive Post-Surgery Support: We provide dedicated follow-up care and rehabilitation, helping you recover efficiently and regain full mobility.