Hip replacement surgery entails removing the worn-out or injured hip joint and replacing it with a prosthesis, an artificial joint. A metal, plastic, or ceramic ball and socket make up a prosthesis. With a hip replacement, the patient can enjoy his daily activities and be pain-free.
Hip pain is frequently brought on by hip arthritis. The joint becomes inflamed and painful when arthritis develops. Osteoarthritis, rheumatoid arthritis, Ankylosing spondylitis, Systemic lupus erythematosus, and Psoriatic arthritis are the five kinds of hip arthritis that can be painful. Although there is no known cure for arthritis, there are therapies and medications available to address its signs and symptoms.
An autoimmune condition that usually affects the joints is rheumatoid arthritis. It is brought on by the body’s immune system mistakenly targeting healthy body components. As a result, there will eventually be bone erosion and joint deformity. It damages the lining of the joints, producing discomfort and swelling.
You can go through in brief about various Hip Problems one can face.
Overview
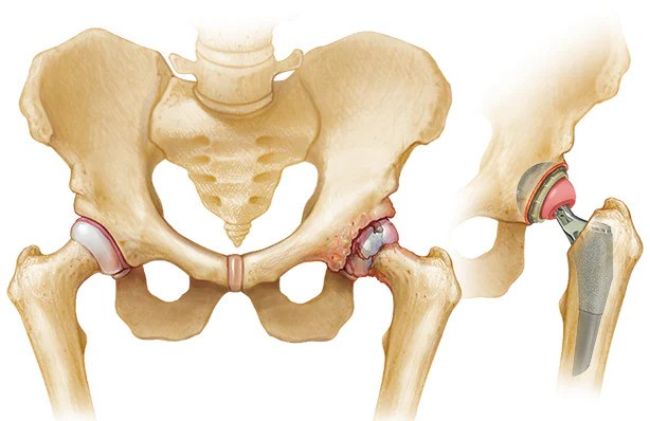
What is Hip Replacement?
Hip replacement surgery involves the extraction and substitution of segments of the pelvis and femur (thighbone) comprising the hip joint. Its primary objective is to alleviate hip discomfort and rigidity triggered by hip arthritis. Additionally, this surgical intervention may be employed to address issues like hip fractures, malformations, and various other conditions. (Locate a specialist in hip replacement at HSS.)
What are the types of Hip replacement?
- Partial hip replacement involves the replacement of just one aspect of your hip joint, typically the rounded top of your thigh bone, known as the femoral head. This surgery is typically reserved for specific types of hip fractures or the removal of certain tumors.
- In contrast, total hip replacement entails the complete replacement of your hip joint with an artificial one. This procedure includes replacing both the top of your thigh bone (femur) and the socket it fits into (acetabulum). The majority of hip replacements performed are total hip replacements.
Symptoms & Causes
What are the symptoms of Hip Replacement?
Symptoms indicating the need for hip replacement include:
- Continuous or recurring pain in the vicinity of the hip joint, that is, in and around
After periods of rest, such as prolonged sitting or upon waking in the morning, you might experience stiffness in your hip. However, this stiffness typically diminishes rapidly once you start moving. Individuals with hip osteoarthritis commonly observe limitations in the range and ease of movement in their hips compared to their usual mobility.
- Challenges in engaging in physical activities like exercise
Engaging in exercise may become more arduous due to restricted mobility and discomfort experienced during physical activities. A limited range of motion in the hip can impede participation in sports that require significant joint flexibility, such as football or running. Additionally, hip discomfort during and after exercise might make it challenging to maintain your usual level of physical activity.
- Alterations in appearance or sound.
In osteoarthritis, joints may occasionally produce a grating or cracking sensation when in motion, known as crepitus. This occurrence isn’t usually a cause for concern, as crepitus can occur in individuals without other symptoms. Additionally, some individuals may notice visible muscle wasting around the affected joint.
- Challenges with balancing on a single leg.
If you struggle to stand on one leg for a duration of one minute, even with support, this could indicate a need for a hip replacement.
- You’re experiencing arthritis in your hip.
Osteoarthritis stands as the primary cause for requiring a hip replacement, yet other conditions such as septic arthritis and rheumatoid arthritis can also lead to damage in the hip joint.
- You’ve exhausted other conservative treatment options:
- Pain from Rest: Treatment for hip pain varies depending on its cause. While many cases of hip pain may resolve with time and rest, persistent pain warrants a visit to your GP, who may suggest further treatment or surgery.
- By Simple Pain- relievers: Pain management involves strengthening weak muscles and reducing stiffness, which may not always be pain-free. Consider using simple pain relievers like paracetamol or Ibuprofen, either orally or in gel form. Consult your GP or pharmacist for appropriate guidance on pain medication suitable for your condition.
- Steroid injections can alleviate swelling and pain in joints. Hydrocortisone is injected directly into the affected joint. These injections are administered by a specially trained doctor, either in a hospital or clinic. While steroid injections can provide short-term relief, addressing underlying causes such as muscle weakness, tightness, excessive strain, or poor posture is essential to prevent symptom recurrence.
- Pain and stiffness are linked to movement.
- Restricted mobility.
- Sleep disturbances.
- Heightened pain, discomfort, and limited mobility stemming from a prior hip injury, like a fractured pelvis, hip fracture, or joint damage.
What are the Causes?
Other conditions that can result in sufficient damage to the hips necessitating a hip replacement include:
- Severe injuries such as car accidents or falls
- Femoroacetabular impingement syndrome (FAI or hip impingement), characterized by an abnormal shape of the hip joint leading to painful bone rubbing
- Hip dysplasia, where the thigh bone (femur) doesn’t properly fit into the hip socket, potentially resulting in dislocation; often present from birth
- Benign (noncancerous) tumors
- Cancer
- Perthes disease, a rare childhood ailment caused by temporary interruption of blood supply to the rounded top of the thigh bone (femur), leading to deformation of the femur’s shape upon restoration of blood flow.
Hip Replacement Diagnosis
Prior to undergoing a hip replacement, you’ll need to consult with an orthopedic surgeon. The surgeon will conduct a thorough examination to assess the condition of your affected hip in comparison to the other one. They’ll evaluate your range of motion, the strength of the supporting muscles in your hip and leg, and delve into your medical history, including symptoms, prior treatments, and medications or supplements you’re taking.
Several diagnostic tests will be necessary before scheduling a hip replacement, which may encompass:
- X-rays of the hip
- Blood tests
- Urinalysis
- Additional imaging scans like MRI or CT scans
- Electrocardiogram (EKG) to evaluate heart health.
Risks/ Benefits Hip Replacement Surgery
Benefits:
Hip surgery can help restore your ability to enjoy your favorite activities. Here are some advantages of undergoing a hip replacement surgery:
- Alleviation of pain in cold
- High success rates
- Improved strength and mobility
- Long-term effectiveness
- Better quality of life
Risks:
However, despite being a common and generally successful procedure, hip replacement surgery carries certain risks, including:
- Nerve damage
- Potential for hip dislocation post-surgery
- Risk of deep vein thrombosis (DVT) and blood clots
- Infection
- Possibility of leg length inequality
- General wear and tear on the prosthetic joint
How to minimize the risk?
To mitigate these risks, patients can take several measures, such as:
- Maintaining a healthy weight
- Preventing falls
- Remaining physically active