Knee Treatment Procedures
Knee Replacement
Knee replacement surgery is a type of knee treatment, which is recommended for advanced or end-stage arthritis. In this type of knee treatment, a surgical procedure is suggested when the patient experiences such severe pain that it significantly interferes with their ability to carry out daily activities.
this type of knee treatment, a surgical procedure is suggested when the patient experiences such severe pain that it significantly interferes with their ability to carry out daily activities.
Because of knee pain, daily tasks like walking and climbing stairs could become challenging, depending on the extent of the damage. As the degradation worsens, bow-legged abnormalities and odd knee noises (crepitus) could be increasingly obvious.
The objective of knee replacement surgery is to regain any lost bone structure or ligament stability, along with repairing damaged cartilage or the surface that facilitates smooth movement. Dr. Preetesh Choudhary is the Best Knee Replacement Surgeon in Indore. Read more about Knee Replacement Surgery.
Knee Preservation- Type of Knee Treatment
Knee joint preservation is the process of restoring the knee joint to its normal range of motion and functionality without the need for replacement. It is a type of knee treatment. The Knee Replacement surgeon, Dr. Preetesh Choudhary can treat knee joint issues while keeping the healthy structure of the damaged joints by using a preservation strategy.
without the need for replacement. It is a type of knee treatment. The Knee Replacement surgeon, Dr. Preetesh Choudhary can treat knee joint issues while keeping the healthy structure of the damaged joints by using a preservation strategy.
The majority of people who require knee joint preservation techniques have abnormalities in the knee’s articular cartilage.
Restoration of articular cartilage provides pain relief, enhances everyday performance, and in some circumstances can even stop or delay the onset of arthritis in the knee joint. Read more about Knee Preservation.
Knee Arthroscopy- Type of Knee Treatment
Arthroscopy surgery is a treatment procedure that does not require the patients to stay overnight in the hospital. Typically, this form of treatment is employed to enhance joint stability and repair injured tissue. Thus, this type of knee treatment, helps the patients to experience less pain and faster healing due to which most knee surgeries require this type of reconstructive orthopaedic surgery. Read More about Knee Arthroscopy
Knee Arthritis Care
Knee arthritis is an inflammation and deterioration of the cartilage of the knee joint. The flexible coating on bone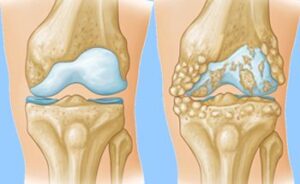 ends known as cartilage acts as a cushion and facilitates the knee’s easy bending and straightening.
ends known as cartilage acts as a cushion and facilitates the knee’s easy bending and straightening.
Knee cartilage covers the top of the tibia, the rear of the kneecap, and the ends of the femur and thighbones (patella). As cartilage deteriorates, the space between the bones diminishes. Bone may rub against bone and develop bone spurs (bumps on the bone) in severe arthritis. Read more about Knee Arthritis & it’s Types.
Types Of Knee Arthritis
- Osteoarthritis of the knee
The knee is one of the most often affected joints by osteoarthritis, the most prevalent type of arthritis. Osteoarthritis results in the thinning of the cartilage in your knee joint and the roughening of the joint surfaces, which causes the knee to move less smoothly than it should and may feel painful and stiff.
Anyone can develop osteoarthritis at any age, although women over 50 are more likely to develop it.
Osteoarthritis can increase a person’s risk of injury or other joint issues, such gout. Our genetics may potentially enhance the likelihood of developing the illness.
Being overweight puts additional strain on weight-bearing joints like your knees, which is one of the causes of osteoarthritis.
- Rheumatoid arthritis
Rheumatoid arthritis, a chronic inflammatory disorder, can affect more than just the joints, potentially impacting various physiological systems such as the skin, eyes, lungs, heart, and blood vessels in certain individuals. In advanced cases, consulting an orthopedic surgeon or a knee replacement surgeon may be necessary to address severe joint damage caused by this condition.
- Post traumatic knee arthritis
Post-traumatic arthritis is joint inflammation that develops after you’ve been injured. It makes your afflicted joints stiff and painful. Although surgery is unlikely, it can take a few months before you feel better. Post-traumatic arthritis can be brought on by any joint injury, including those sustained in sports injury or car accidents. Knee treatment is required for such cases.
ACL Reconstruction
Anterior cruciate ligament (ACL) surgery is a type of knee treatment, which entails either repairing or reconstructing the ACL, a vital soft tissue connection between the femur and tibia within the knee joint. ACL tears, whether partial or full, are a frequent occurrence among athletes. Complete ACL injuries are often treated with an ACL reconstruction operation by sports medicine doctors and orthopaedic surgeons, in which the torn ligament is replaced with a tissue graft to replicate the original ACL. Read more about ACL Reconstruction.
Meniscal Tear
Your knee has a piece of cartilage that stabilises and cushions the joint. It shields the bones from deterioration. But all it takes to tear the meniscus is a nice twist of the knee. In rare instances, a fragment of the torn cartilage comes away and becomes caught in the knee joint, locking it.
Both contact sports like football and non-contact sports demanding jumping and cutting, like volleyball and soccer, frequently result in meniscus injuries. They frequently occur concurrently with other knee injuries, such as an anterior cruciate ligament (ACL) damage, and can occur when a runner abruptly changes direction while jogging. Meniscus tears pose a particular threat to older athletes due to the natural weakening of the meniscus as one ages. Read more about Meniscal Tear.
Cartilage Defects
Damage to the articular cartilage, the smooth material that covers the ends of the bones to prevent them from rubbing against one another, results in cartilage abnormalities of the knee. Degenerative cartilage defects are the consequence of wear and tear, while traumatic cartilage defects are brought on by an injury such as a fall onto the knee, a jump, or a sudden change in direction while playing a sport. Due to the lack of nerves in cartilage, such injuries do not necessarily result in acute symptoms. However, over time, cartilage issues can impair normal joint performance, resulting in discomfort, inflammation, a grinding sensation in the knee, and restricted mobility.
Knee Treatment of Cartilage Defects
- Debridement
Debridement may be an option for older patients with minor symptoms and lesser cartilage abnormalities. - Microfracture
An arthroscopic treatment called microfracture is used to restore damaged knee cartilage. - Osteochondral Autograft Transplantation (OATS)
In this procedure, healthy cartilage is removed from a patient’s non-weight-bearing area and transplanted to the damaged area. - Autologous Chondrocyte Implantation
A sample of healthy cartilage is taken out during this process, reproduced in large quantities outside the body, and then re-implanted onto the nearby bone. This recently developed cartilage wraps the bone, providing support and protection.
Read more about Cartilage Defects.
Multi-Ligament Injuries / Reconstruction
When damage occurs to two or more of the main ligaments in the knee—the anterior cruciate ligament (ACL), posterior cruciate ligament (PCL), medial collateral ligament (MCL), and posterior lateral complex (PLC)—it is termed as a multiple ligament knee injury (MLKI). Such injuries can arise from various sources of trauma, ranging from sports-related incidents to high-impact accidents like car crashes or falls from significant heights. As a result of ultra-low velocity trauma, typically in the form of hyperextension. PCL Injuries & Multi- ligament Injuries/ Reconstruction.