Signs and Symptoms of a Labrum Tear you shouldn’t ignore!
What is Labrum Tear?
A Labrum Tear refers to the damage of the labrum, a cartilage that lines the socket of a joint. The labrum acts as a cushion, stabilizes the joint, and provides a smooth surface for joint movement. This tear is most commonly found in the hip and shoulder joints, as these are ball-and-socket joints supported by the labrum.
1. Shoulder Labrum Tear
A shoulder labrum tear is an injury to the ring of cartilage that lines the socket of the shoulder joint. The two most common types of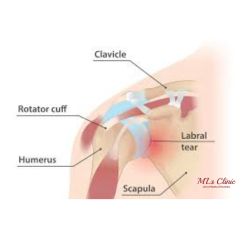 shoulder labrum tears are:
shoulder labrum tears are:
-
- SLAP Tear – SLAP stands for Superior Labrum Anterior and Posterior. This type of tear affects the upper labrum where the bicep tendon attaches to the shoulder.
- Bankart Tear – This tear is most common in younger patients who dislocate their shoulder. It affects the lower labrum when the shoulder joint ball slips out of the socket, pulling and tearing the lower labrum.
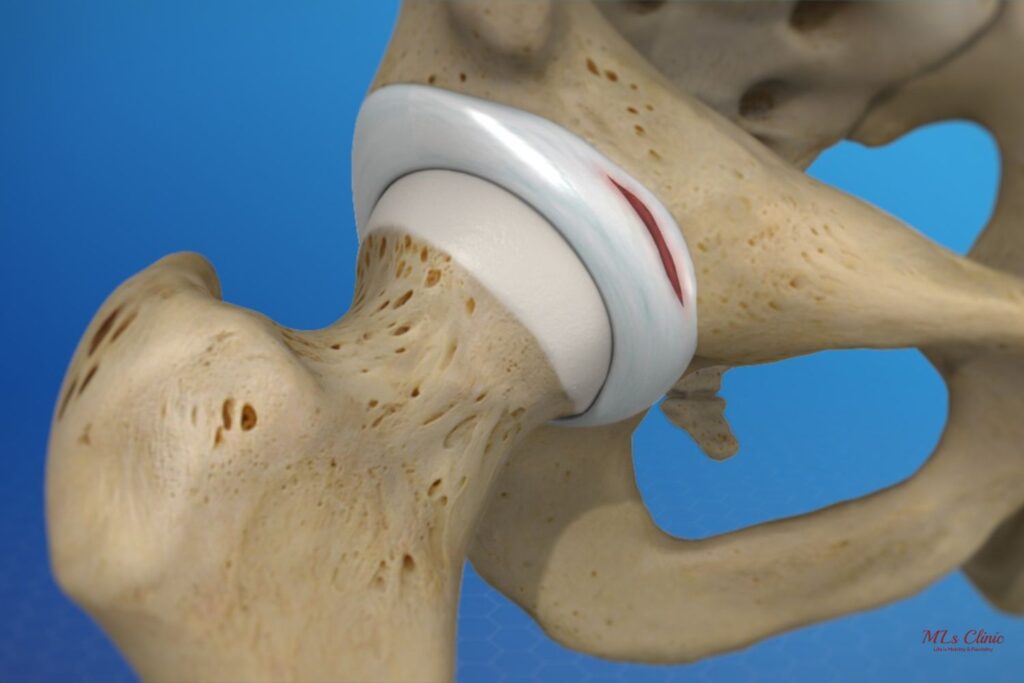
2. Hip Labrum Tear
A hip labrum tear, also medically known as acetabular labral tear, is a common injury where the hip labrum lines the socket of the hip joint.
What Causes a Labrum Tear?
A labrum tear can occur due to several factors, including:
- Age – Age-related degeneration of the labrum weakens the cartilage over time, making it prone to tears.
- Overuse – Repetitive motion activities, such as throwing, swimming, or running, can lead to labrum overuse and eventual tears.
- Trauma – Sudden falls or impacts, especially in contact sports like hockey, basketball, or football, can cause trauma to the shoulder or hip, leading to a labrum tear.
- Abnormal Structure – Certain conditions such as hip impingement or shoulder instability increase the risk of labrum tears.
Treatment Options for a Labrum Tear
The treatment for a labrum tear depends on the severity of the injury and the intensity of your activity. The following are some treatment options:
-
Non-Surgical Treatments:
- Physical Therapy – Physiotherapy exercises focus on strengthening the muscles around the joint to improve stability and reduce strain on the labrum. It is an important part of non-surgical treatment for a labrum tear.
- Rest – Providing rest to the affected joint by avoiding activities that worsen the situation is crucial for healing.
- Medications – Anti-inflammatory medications or cortisone injections help reduce pain and provide temporary relief.
-
Surgical Treatment:
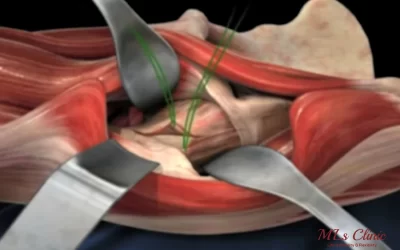
Surgery is often recommended for patients who are highly active, such as athletes, or for those with significantly unstable joints. Arthroscopic Surgery is the best option for repairing or removing the damaged labrum. For the best treatment for Labrum Tear in Indore, visit MLs Clinic, one of the leading Orthopedic Clinics in the city.
Conclusion
A labrum tear in either the shoulder or hip joint can severely impact your quality of life, but with early diagnosis and appropriate treatment, you can recover fully and return to normal activities. To reduce the risk of a labrum tear, focus on maintaining joint stability, providing proper rest, and using protective gear during physical activities. However, if you continue to experience pain or discomfort, consult Indore’s leading orthopedic surgeon, Dr. Preetesh Choudhary, for an expert diagnosis and treatment plan.